Clean Resources
We are Providing Integrated Solutions for Diverse Industries: Empowering Sustainable Futures.

Captainwatt
Industrial Overview
Exploring Our Industries
Fields we work on
Renewable Energy
E-Mobility
Military Support Systems

What is Hydrogen?
What Does Hydrogen Have to Do with Climate Neutrality?
Hydrogen can help make certain emission-intensive products and processes—ones that modern societies are unwilling or unable to abandon—more climate-friendly.
What Does Hydrogen Have to Do with Renewably Generated Electricity?
Three steps to using hydrogen as a storage system
1.
Electrolysis with water and renewable electricity.
2.
Storage and transport of gaseous hydrogen.
3.
Re-conversion of hydrogen into
electricity.
Green and Blue: What Do Hydrogen Colors Mean?
- Green Hydrogen is produced with renewable energy and is virtually emission-free. While some emissions may occur during plant construction, this is common to all infrastructure.
- Blue Hydrogen, like gray hydrogen, is produced using natural gas. CO₂ emissions are captured and stored underground, making it “climate-neutral” in theory. However, this is controversial due to additional emissions from natural gas use and a lack of large-scale production facilities.
- Pink Hydrogen is produced using nuclear power.
- Yellow Hydrogen is produced using grid electricity (a mix of fossil, nuclear, and renewable sources).

Why is Blue Hydrogen Controversial?

What Role Does Hydrogen Play in a Climate-Neutral Industry?
- In the chemical industry, green hydrogen can be used to produce green ammonia—an essential input and the most CO₂-intensive petrochemical product.
- In the steel industry, hydrogen can replace coal in blast furnaces or natural gas in direct reduction plants.
Engagement of H₂ Generators and Fuel Cells
Longer runtimes
Lower noise
Reduced emissions

Hydrogen Generators and Fuel Cells: Key Benefits
Energy Efficiency
Consume 35% less energy than diesel generators • Zero
Future-Ready
Compatible with renewable methanol for future compliance
Harmful Emissions
No NOₓ, SOₓ, or particulates; 28% lower CO₂ emissions
Carbon Neutral Potential
When using renewable methanol, emissions can be minimal, and carbon capture is feasible
Reliable Operation
Few moving parts = low maintenance
costs

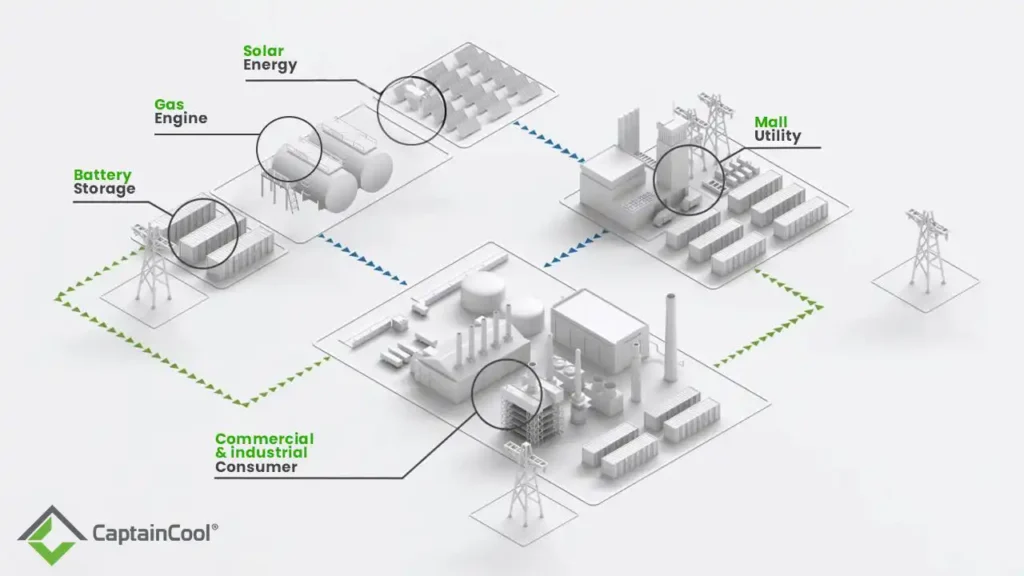
Modes of operands for the green energy.
1.
Deployment of containerized electrolyses on site green energy H2 generation
2.
Storage & logistics H2 SKU’S Insulated Tanks & cryogenic bottles.
3.
Storage alternative generated O2 application medical gas.
4.
Inlet clean energy H2 use for Gas fired engines turbine containerized plant for electricity generation.
5.
Usage direct electricity to the turnkey plants & off shower applications.
6.
Charging AC2DC containers BESS paring with GT & Solar generated energy.
7.
E-mobility charging stations outlets & mobile DC2DC – Software support
8.
ENERGY STORAGE AS- A-SERVICE (ESAAS)
9.
The green energy net zero carbon module SOP carbon commodities carbon credit certificate.
10.
Collaboration R & D good laboratories prototype system integrations empowering youth as nation’s builder.
11.
Develop self reliant renewable generation equipments meet suitable to Indigenous geographical paradox.


